1.源码模块
源码项目主要有以下四个模块:
1. spring-boot-project:整个SpringBoot框架全部功能在这个模块实现,SpringBoot项目95%的代码都在这里实现,源码总共有26万行左右。
2. Spring-boot-samples:包含了各种各样使用SpringBoot的简单demo,调试阅读源码的时候可以充分利用该模块。
3. Spring-boot-sample-invoker:这个模块是跟samples模块有关,根pom.xml中有这么一句话:Samples are built via the invoker plugin,该模块无代码。
4. Spring-boot-tests:SpringBoot的测试模块,跟部署测试和集成测试有关。SpringBoot的全部功能在spring-boot-project模块实现,因此下面重点来介绍下 spring-boot-project 模块。
2.spring-boot-project 模块
1) spring-boot-parent
这个模块没有代码,是spring-boot模块的父项目,被其他子模块继承。
2) spring-boot
这个模块是SpringBoot项目的核心,一些基础核心的功能都在这里实现,为SpringBoot的其他模块组件功能提供了支持,主要包括以下核心功能:
1. SpringApplication类,这个是SpringBoot的启动类,提供了一个静态的run方法来启动程序,该类主要用来创建并且刷新Spring容器ApplicationContext.
2. 支持选择不同的容器比如Tomcat,Jetty等来作为应用的嵌入容器。
3. 外部配置支持,执行java -jar xxx.jar命令时可以带一些参数,比如执行java -jar demo.jar --server.port=9999来将应用端口修改为9999.
4. 内置了一些SpringBoot启动时的生命周期事件和一些容器初始化器(ApplicationContext initializers),来执行一些SpringBoot启动时的初始化逻辑。3) spring-boot-autoconfigure
这个模块跟SpringBoot的自动配置有关。比如SpringBoot能基于类路径来自动配置某个项目模块,自动配置最为关键的注解是@EnableAutoConfiguration,这个注解能触发Spring上下文的自动配置。另外一个重要的注解是@Conditional。
除了根据类路径来进行自动配置外,还有根据容器中是否存在某个bean等方式来进行自动配置。
4) spring-boot-starters
这个模块是跟SpringBoot的起步依赖有关。SpringBoot通过提供各种各样的起步依赖降低项目依赖的复杂度。起步依赖其实就是利用maven项目模型将其他相关的依赖给聚合起来,里面各种依赖的版本号都给定义好,避免用户在引入依赖时出现各种版本冲突,方便了我们的使用。
比如说:要用到activemq时,可以直接引入spring-boot-starter-activemq起步依赖即可,若SpringBoot官网或第三方组织没有提供相应的SpringBoot起步依赖时,可以进行定制自己的起步依赖。注意,该模块没有代码,主要是通过maven的pom.xml来组织各种依赖。
5) spring-boot-cli
Spring Boot CLI是一个命令行工具,如果想使用Spring快速开发,可以使用它。允许运行Groovy脚本,这意味着有一个熟悉的类似Java的语法,而没有那么多样板代码。还可以引导一个新项目或编写自己的命令。
6) spring-boot-actuator
SpringBoot的监控模块。可以通过HTTP端点或JMX等来管理和监控应用。审计、运行状况和度量收集可以自动应用到应用程序。这个监控模块是开箱即用的,提供了一系列端点包括HealthEndpoint, EnvironmentEndpoint和BeansEndpoint等端点。
7) spring-boot-actuator-autoconfigure
这个模块为spring-boot-actuator监控模块提供自动配置的功能,通常也是根据类路径来进行配置。比如Micrometer存在于类路径中,那么将会自动配置MetricsEndpoint。
8) spring-boot-test
这个模块是spring-boot 测试有关的模块,包含了一些帮助测试的核心类和注解(比如@SpringBootTest)。
9) spring-boot-dependencies
这个模块没有代码,主要是定义了一些SpringBoot的maven相关的一些依赖及其版本。
10) spring-boot-devtools
这个模块跟SpringBoot的热部署有关,即修改代码后无需重启应用即生效。
11) spring-boot-docs
这个是跟文档相关的模块。
12) spring-boot-properties-migrator
SpringBoot 对外部化配置原生支持迁移功能,所谓迁移,具体是指对应配置的属性名变动,仍可以使用原来的属性名配置。
在 spring-configuration-metadata.json 的信息可以辅助 IDE 进行配置的提示,也可以用来完成配置的迁移。
13) spring-boot-test-autoconfigure
这个模块是跟spring-boot-test的测试的自动配置有关。
14) spring-boot-tools
这个模块是SpringBoot的工具相关的模块,提供了加载,maven插件,Gradle插件,metadata和后置处理相关的支持。
上面介绍了这么多spring-boot-project模块下的子模块,真正要重点分析的模块有spring-boot,spring-boot-autoconfigure,spring-boot-starters和spring-boot-actuator模块。

3. SpringBoot模块间的POM关系
根据上面SpringBoot的各个模块的具体功能,来看下SpringBoot模块的pom之间的关系。
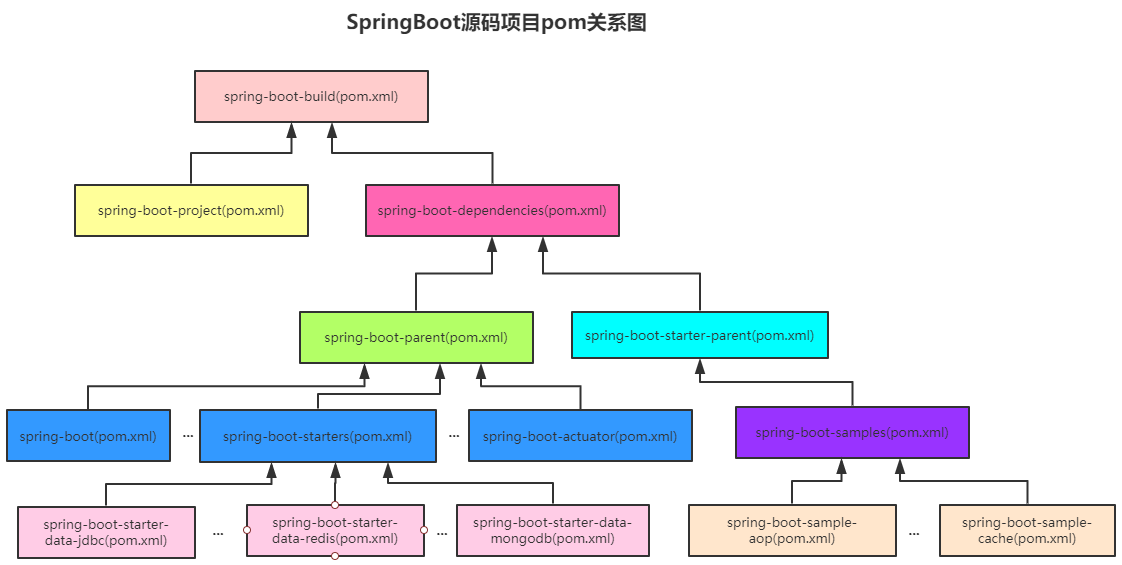
根据上图可以看到:
1. spring-boot-build(pom.xml)是项目的根pom,其子pom有spring-boot-project(pom.xml)和spring-boot-dependencies(pom.xml);
2. spring-boot-dependencies(pom.xml)主要定义了SpringBoot项目的各种依赖及其版本,其子pom有spring-boot-parent(pom.xml)和spring-boot-starter-parent(pom.xml);
3. spring-boot-project(pom.xml)有聚合module的作用,其子模块并不继承于它,而是继承于spring-boot-parent(pom.xml);
4. spring-boot-parent(pom.xml)是spring-boot-project(pom.xml)的子module,但继承的父pom为spring-boot-dependencies(pom.xml),其定义了一些properties等相关的东西。其子pom为spring-boot-project(pom.xml)的子module(注意除去spring-boot-dependencies(pom.xml)),比如有spring-boot(pom.xml),spring-boot-starters(pom.xml)和spring-boot-actuator(pom.xml)等;
5. spring-boot-starters(pom.xml)是所有具体起步依赖的父pom,其子pom有spring-boot-starter-data-jdbc(pom.xml)和spring-boot-starter-data-redis(pom.xml)等。
6. spring-boot-starter-parent(pom.xml),是所有具体SpringBoot项目的父pom,比如SpringBoot自带的样例的spring-boot-samples(pom.xml)是继承于它的。SpringBoot的各模块之间的pom关系有点复杂,可以打开idea的项目,逐个去捋一下。SpringBoot的父pom就是做一些版本管理,聚合模块之间的事情。


评论加载中