上一篇分析了SpringBoot启动时广播生命周期事件的原理,关键步骤总结:
- 为广播SpringBoot内置生命周期事件做前期准备:
1)首先加载ApplicationListener监听器实现类;
2)其次加载SPI扩展类EventPublishingRunListener。 - SpringBoot启动时利用
EventPublishingRunListener广播生命周期事件,然后ApplicationListener监听器实现类监听相应的生命周期事件执行一些初始化逻辑的工作。
1.SpringBoot生命周期事件源码分析
SpringBoot的生命周期事件,类结构图:
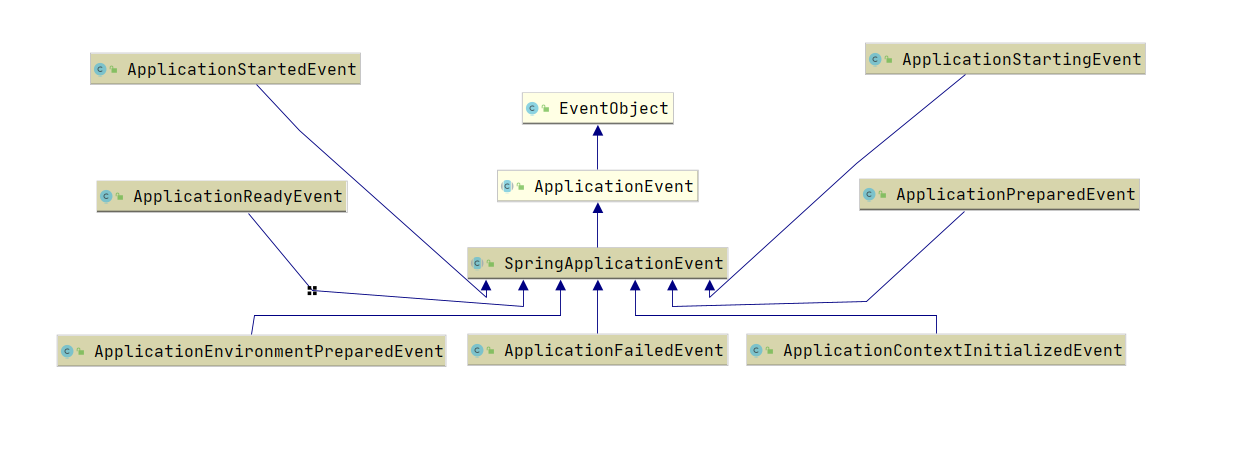
由上图可以看到事件类之间的关系:
- 最顶级的父类是JDK的事件基类
EventObject; - 然后Spring的事件基类
ApplicationEvent继承了JDK的事件基类EventObject; - 其次SpringBoot的生命周期事件基类
SpringApplicationEvent继承了Spring的事件基类ApplicationEvent; - 最后SpringBoot具体的7个生命周期事件类再继承了SpringBoot的生命周期事件基类
SpringApplicationEvent。
1.1 JDK的事件基类EventObject
EventObject类是JDK的事件基类,是所有Java事件类的基本,即所有的Java事件类都直接或间接继承于该类,源码如下:
1 | public class EventObject implements java.io.Serializable { |
可以看到EventObject类只有一个属性source,这个属性是用来记录最初事件是发生在哪个类。
比如在SpringBoot启动过程中会触发ApplicationStartingEvent事件,而这个事件最初是在SpringApplication类中触发的,因此source就是SpringApplication对象。
1.2 Spring的事件基类ApplicationEvent
ApplicationEvent继承了JDK的事件基类EventObject类,是Spring的事件基类,被所有Spring的具体事件类继承,源码如下:
1 | public abstract class ApplicationEvent extends EventObject { |
可以看到ApplicationEvent有且仅有一个属性timestamp,该属性是用来记录事件发生的时间。
1.3 SpringBoot的事件基类SpringApplicationEvent
SpringApplicationEvent类继承了Spring的事件基类ApplicationEvent,是所有SpringBoot内置生命周期事件的父类,源码如下:
1 | ("serial") |
可以看到SpringApplicationEvent有且仅有一个属性args,该属性就是SpringBoot启动时的命令行参数即标注@SpringBootApplication启动类中main函数的参数。
2.SpringBoot具体的生命周期事件类
接下来分析一下SpringBoot内置生命周期事件即SpringApplicationEvent的7个具体子类。
2.1 ApplicationStartingEvent
1 | public class ApplicationStartingEvent extends SpringApplicationEvent { |
SpringBoot开始启动时便会发布ApplicationStartingEvent事件,其发布时机在环境变量Environment或容器ApplicationContext创建前但在注册ApplicationListener具体监听器之后,标志标志SpringApplication开始启动。
2.2 ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent
1 | public class ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent extends SpringApplicationEvent { |
可以看到ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent事件多了一个environment属性,作用是利用事件发布订阅机制,相应监听器可以从ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent事件中取出environment变量,然后可以为environment属性增加属性值或读出environment变量中的值。
例如:
ConfigFileApplicationListener监听器就是监听了ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent事件,然后取出ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent事件的environment属性,然后再为environment属性增加application.properties配置文件中的环境变量值。
当SpringApplication已经开始启动且环境变量Environment已经创建后,并且为环境变量Environment配置了命令行和Servlet等类型的环境变量后,此时会发布ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent事件。
监听ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent事件的第一个监听器是ConfigFileApplicationListener,因为是ConfigFileApplicationListener监听器还要为环境变量Environment增加application.properties配置文件中的环境变量;此后还有一些也是监听ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent事件的其他监听器监听到此事件时,此时环境变量Environment几乎已经完全准备好了。
思考: 监听同一事件的监听器们执行监听逻辑时是有顺序的,可以想一下这个排序逻辑是什么时候排序的?还有为什么要这样排序呢?
2.3 ApplicationContextInitializedEvent
1 | public class ApplicationContextInitializedEvent extends SpringApplicationEvent { |
可以看到ApplicationContextInitializedEvent事件多了个ConfigurableApplicationContext类型的context属性,context属性的作用同样是为了相应监听器可以拿到这个context属性执行一些逻辑。
ApplicationContextInitializedEvent事件在ApplicationContext容器创建后,且为ApplicationContext容器设置了environment变量和执行了ApplicationContextInitializers的初始化方法后但在bean定义加载前触发,标志ApplicationContext已经初始化完毕。
扩展: 可以看到
ApplicationContextInitializedEvent是在为context容器配置environment变量后触发,此时ApplicationContextInitializedEvent等事件只要有context容器的话,那么其他需要environment环境变量的监听器只需要从context中取出environment变量即可,从而ApplicationContextInitializedEvent等事件没必要再配置environment属性。
2.4 ApplicationPreparedEvent
1 | public class ApplicationPreparedEvent extends SpringApplicationEvent { |
同样可以看到ApplicationPreparedEvent事件多了个ConfigurableApplicationContext类型的context属性,多了context属性的作用是能让监听该事件的监听器们能拿到context属性,监听器拿到context属性一般有如下作用:
- 从事件中取出
context属性,然后可以增加一些后置处理器,比如ConfigFileApplicationListener监听器监听到ApplicationPreparedEvent事件后,然后取出context变量,通过context变量增加了PropertySourceOrderingPostProcessor这个后置处理器; - 通过
context属性取出beanFactory容器,然后注册一些bean,比如LoggingApplicationListener监听器通过ApplicationPreparedEvent事件的context属性取出beanFactory容器,然后注册了springBootLoggingSystem这个单例bean; - 通过
context属性取出Environment环境变量,然后就可以操作环境变量,比如PropertiesMigrationListener。
ApplicationPreparedEvent事件在ApplicationContext容器已经完全准备好时但在容器刷新前触发,在这个阶段bean定义已经加载完毕还有environment已经准备好可以用了。
2.5 ApplicationStartedEvent
1 | public class ApplicationStartedEvent extends SpringApplicationEvent { |
ApplicationStartedEvent事件将在容器刷新后但ApplicationRunner和CommandLineRunner的run方法执行前触发,标志Spring容器已经刷新,此时容器已经准备完毕了。
扩展: 这里提到了
ApplicationRunner和CommandLineRunner接口有啥作用呢?一般会在Spring容器刷新完毕后,此时可能有一些系统参数等静态数据需要加载,此时就可以实现了ApplicationRunner或CommandLineRunner接口来实现静态数据的加载。
2.6 ApplicationReadyEvent
1 | public class ApplicationReadyEvent extends SpringApplicationEvent { |
ApplicationReadyEvent事件在调用完ApplicationRunner和CommandLineRunner的run方法后触发,此时标志SpringApplication已经正在运行。
2.7 ApplicationFailedEvent
1 | public class ApplicationFailedEvent extends SpringApplicationEvent { |
可以看到ApplicationFailedEvent事件除了多了一个context属性外,还多了一个Throwable类型的exception属性用来记录SpringBoot启动失败时的异常。
ApplicationFailedEvent事件在SpringBoot启动失败时触发,标志SpringBoot启动失败。
总结
SpringBoot启动过程中要触发的各种生命周期事件
| 发布顺序 | 时间 | 用途 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | ApplicationStartingEvent | 在SpringApplication启动时,在环境变量Environment或者容器ApplicationContext创建前触发,标志SpringApplication开始启动。 |
| 2 | ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent | 当SpringApplication已经开始启动且环境变量Environment已经准备好时触发,标志环境变量已经准备好。 |
| 3 | ApplicationContextInitializedEvent | ApplicationContextInitializers的初始化方法已经被调用,即从spring.factories中加载的initializers已经执行ApplicationContext初始化逻辑但在bean定义加载前触发,标志ApplicationContext已经初始化完毕。 |
| 4 | ApplicationPreparedEvent | 在Spring容器刷新refresh前触发 |
| 5 | ApplicationStartedEvent | 在spring容器刷新后触发,但在调用ApplicationRunner和CommandLineRunner的run方法调用前触发,标志spring容器已经刷新,此时所有的bean实例等都已经加载了。 |
| 6 | ApplicationReadyEvent | 只要SpringApplication可以接收服务请求时即调用完ApplicationRunner和CommandLineRunner的run方法后触发,此时标志SpringApplication已经正在运行,即启动成功。 |
| 7 | ApplicationFailedEvent | 若SpringApplication未能成功启动时则会catch住异常发布ApplicationFailedEvent事件,标志ApplicationFailedEvent启动失败。 |


评论加载中